
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NEET MCQ
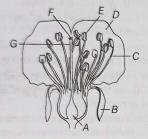
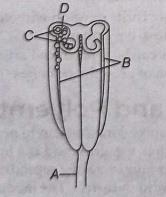
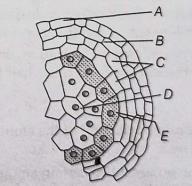
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants involves the production of male and female gametes, fertilization and the development of seeds and fruits. The male reproductive part is the stamen, which consists of the anther and filament. The anther produces pollen grains that contain the male gametes. The female reproductive part is the pistil, which includes the stigma, style and ovary. The ovary contains ovules, each with a female gamete.
Pollination occurs when pollen from the anther is transferred to the stigma. This can happen through wind, water, insects or other animals. Once on the stigma, pollen grains germinate and form pollen tubes that grow down the style to reach the ovary. Fertilization occurs when the male gamete fuses with the female gamete in the ovule, forming a zygote. The zygote develops into an embryo and the ovule becomes a seed. The ovary matures into a fruit, protecting the seeds and aiding in their dispersal.
| NEET 2025 Exam Important Links | |
|---|---|
| NEET 2025 Updated Syllabus | NEET Eligibility Criteria 2025 |
| Biology Preparation | Chemistry NEET Preparation |
| NEET Preparation tips for 2025 | NEET Result 2024 |
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants MCQs for NEET
Enhance your preparation with Arexiq’s Mock Test Series where we provide solutions to various MCQs like we provide in this post Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NEET MCQ”. Our expert teachers explain the concepts thoroughly, making it easy for you to understand. We offer many types of questions ensuring a clear grasp of concepts.
FAQs about Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Q1: What is sexual reproduction in flowering plants?
Answer: Sexual reproduction in flowering plants involves the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote, which eventually develops into a seed. This process includes pollination, fertilization, seed development and fruit formation.
Q2: What are the main parts involved in the sexual reproduction of flowering plants?
Answer: The main parts involved are the stamen (male reproductive organ) which consists of the anther and filament and the pistil (female reproductive organ) which includes the stigma, style and ovary.
Q3: What is pollination?
Answer: Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther (male part) to the stigma (female part) of a flower. It can be done by wind, water, insects or animals.
Q4: What is fertilization in flowering plants?
Answer: Fertilization in flowering plants is the process where the male gamete (sperm) from the pollen grain fuses with the female gamete (egg) in the ovule to form a zygote.
Q5: What is the role of the pollen tube?
Answer: The pollen tube grows from the pollen grain on the stigma down through the style to the ovary, allowing the male gametes to reach the ovule for fertilization.
Q6: What happens after fertilization?
Answer: After fertilization, the ovule develops into a seed and the ovary matures into a fruit, which protects the seed and aids in its dispersal.
Q7: What is double fertilization?
Answer: Double fertilization is a unique process in flowering plants where one sperm fertilizes the egg, forming a zygote, while the other sperm fuses with two polar nuclei to form the endosperm, which nourishes the developing embryo.
Q8: Why is the endosperm important?
Answer: The endosperm provides essential nutrients to the developing embryo, supporting its growth until it can perform photosynthesis on its own.
Q9: What are the types of pollination?
Answer: There are two main types of pollination: self-pollination (pollen from the same flower or plant) and cross-pollination (pollen from a different plant).
Q10: What are some adaptations of flowers for pollination?
Answer: Flowers have various adaptations for pollination, such as bright colors, sweet nectar, fragrances and specific shapes to attract pollinators like bees, butterflies, birds and bats.


