
Reproduction in Organisms MCQ for NEET
Reproduction is a fundamental process in all living organisms, ensuring the continuation of species from one generation to the next. It can occur in two primary forms: asexual and sexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction, a single organism produces offspring that are genetically identical to itself, common in unicellular organisms like bacteria and some plants. Methods of asexual reproduction include binary fission, budding and fragmentation. This type of reproduction allows for rapid population growth and requires less energy.
Sexual reproduction, on the other hand, involves the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in offspring with genetic variation. This process typically occurs in higher plants and animals, including humans. Sexual reproduction enhances genetic diversity, which is important for the adaptability and survival of species in changing environments.
| NEET 2025 Exam Important Links | |
|---|---|
| NEET 2025 Updated Syllabus | How to read NCERT Biology for NEET |
| Biology Preparation | NEET Eligibility Criteria 2025 |
| NEET Preparation tips for 2025 | NEET Result 2024 |
Reproduction in Organisms MCQ for NEET
“Reproduction in Organisms” is a fundamental topic in the NEET syllabus as it lays the foundation for understanding how life continues across generations. This topic covers the various methods by which organisms reproduce, including both asexual and sexual reproduction.
A clear grasp of these concepts is essential because they explain how genetic material is passed from one generation to the next, ensuring the survival and evolution of species. It also introduces students to important concepts like cell division, fertilization and the development of offspring, all of which are important for understanding more complex biological processes.
Reproduction in Organisms MCQ for NEET

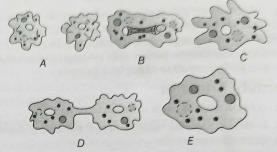
A. Daughter cells formation
B. Enlargement of nucleus
C. Parent cell
D. Constricted cell formation
E. Minimisation of pseudopodia
Arrange the figures and processes in the correct sequence and select the correct answer.
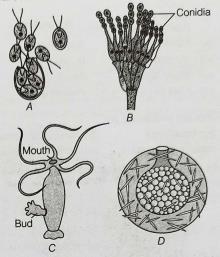
A. Zoospore of Chlamydomonas.
B. Conidia of Penicillium.
C. Buds in Hydra.
D. Gemmules in sponge.
All the above are
Enhance your preparation with Arexiq’s Mock Test Series where we provide solutions to various MCQs like we provide in this post “Reproduction in Organisms NEET MCQ”. Our expert teachers explain the concepts thoroughly, making it easy for you to understand. We offer many types of questions ensuring a clear grasp of concepts.
FAQs
1.What is the significance of studying reproduction in organisms for NEET?
Answer. Studying reproduction in organisms is important for NEET as it covers essential concepts related to how different organisms reproduce, which is important for understanding genetics, evolution and biodiversity.
2.What are the two main types of reproduction?
Answer. The two main types of reproduction are asexual reproduction, where offspring are produced from a single parent without the involvement of gametes and sexual reproduction, where offspring are produced through the fusion of male and female gametes.
3. Why is sexual reproduction considered more advantageous than asexual reproduction?
Answer. Sexual reproduction is considered more advantageous because it introduces genetic variation, which increases the adaptability and survival of species in changing environments.
4. What is the difference between oviparous and viviparous organisms?
Answer. Oviparous organisms lay eggs that develop and hatch outside the mother’s body, while viviparous organisms give birth to live young after internal development.
5. How do unicellular organisms like bacteria reproduce?
Answer. Unicellular organisms like bacteria primarily reproduce through asexual methods such as binary fission, where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
6. What is the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction?
Answer. Meiosis is essential in sexual reproduction as it reduces the chromosome number by half, ensuring that the offspring have the correct number of chromosomes after the fusion of gametes.


