
Plant Growth and Development Biology MCQ for NEET
Plant growth and development are important processes involving cellular activities that lead to an increase in size and complexity of the plant body. Growth is defined as permanent increase in size and volume due to cell division and enlargement. It occurs in specific regions called meristems, which are present at the tips of roots and shoots (apical meristems) and along the sides (lateral meristems). This process is influenced by various factors, including light, water, temperature and nutrients.
Development, on the other hand, refers to the progression of plants through different stages of life, from seed germination to senescence. It encompasses not only growth but also differentiation, where cells become specialized to perform specific functions. During development, plants undergo morphogenesis, forming structures like leaves, flowers and fruits. This process is tightly regulated by genetic and environmental factors, ensuring that plants adapt to their surroundings and optimize their growth for survival and reproduction.
| NEET 2025 Exam Important Links | |
|---|---|
| NEET 2025 Updated Syllabus | NEET Eligibility Criteria 2025 |
| Biology Preparation | Chemistry NEET Preparation |
| NEET Preparation tips for 2025 | NEET Result 2024 |
Plant Growth and Development Biology MCQ for NEET
The topic of “Plant Growth and Development” is an important part of the NEET syllabus. It forms the foundation for understanding the complex physiological processes that govern plant life. This area covers essential concepts such as the stages of plant growth, the roles of various hormones and the environmental factors that influence development. A strong grasp of these principles is vital for aspiring medical students, as it enhances their understanding of broader biological systems and their interconnectedness.
Moreover, knowledge of plant growth and development has practical applications in agriculture, biotechnologyand environmental science. Understanding how plants grow and respond to their environment can lead to innovations in crop production, sustainable farming practices and the development of new medicinal compounds.
Plant Growth and Development Biology MCQ for NEET
Enhance your preparation with Arexiq’s Mock Test Series where we provide solutions to various MCQs like we provide in this post “Plant Growth and Development NEET MCQ”. Our expert teachers explain the concepts thoroughly, making it easy for you to understand. We offer many types of questions ensuring a clear grasp of concepts.
FAQs about Plant Growth and Development
1.What is plant growth and development?
Answer. Plant growth and development refer to the processes by which plants increase in size, mature, and undergo differentiation to form various tissues and organs. Growth involves cell division and expansion, while development encompasses the formation of structures and functions.
2. What are the primary factors influencing plant growth?
Answer. The primary factors influencing plant growth include light, water, temperature, nutrients, and atmospheric gases. Each of these factors can affect photosynthesis, respiration and overall plant health.
3. What are the main plant hormones involved in growth and development?
Answer. The main plant hormones are:
- Auxins: Promote cell elongation and are involved in apical dominance.
- Gibberellins: Stimulate stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering.
- Cytokinins: Promote cell division and can delay leaf senescence.
- Abscisic Acid (ABA): Inhibits growth and helps plants respond to stress.
- Ethylene: Influences fruit ripening and leaf abscission.
4. What is phototropism and how does it work?
Answer. Phototropism is the growth response of plants towards or away from light. It is primarily mediated by auxins. When light is detected, auxins move to the shaded side of the plant, causing cells to elongate more on that side and resulting in the plant bending towards the light.
5. What is the difference between primary and secondary growth in plants?
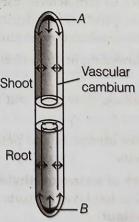
Answer. Primary growth refers to the elongation of stems and roots, which occurs at the apical meristems (tips of shoots and roots). Secondary growth refers to the increase in thickness or girth of stems and roots, which occurs in the lateral meristems (cambium).
6. How do plants respond to environmental stress?
Answer. Plants respond to environmental stress through various mechanisms such as altering their growth patterns, producing stress hormones like abscisic acid and activating stress-responsive genes. They may also develop physical adaptations like thicker cuticles or deeper root systems.
7. What is the role of photosynthesis in plant growth?
Answer. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. This process provides the energy and organic compounds necessary for growth, development and overall metabolism.
8. How do plants regulate water loss?
Answer. Plants regulate water loss through structures like stomata and the cuticle. Stomata are small openings on leaves that can open or close to control gas exchange and water loss. The cuticle is a waxy layer on the surface of leaves that reduces water evaporation.
9. What is the significance of seed dormancy?
Answer. Seed dormancy is a period during which seeds remain inactive and do not germinate, even under favorable conditions. This mechanism helps seeds avoid germinating during unfavorable conditions and ensures they only sprout when the environment is suitable for growth.
10. How do plants undergo flowering and what triggers it?
Answer. Flowering is triggered by various environmental signals, such as light duration (photoperiod), temperature and water availability. Flowering is regulated by genes and hormones that initiate the transition from vegetative growth to reproductive development


