
Breathing and Exchange of Gases NEET Biology MCQ with Answers
Breathing and the exchange of gases are important processes for maintaining life. Breathing involves the intake of oxygen and the expulsion of carbon dioxide through the respiratory system. The main organs involved are the lungs, which are designed to maximize the exchange of gases. Oxygen from the air we breathe enters the lungs and passes into the blood, while carbon dioxide from the blood is expelled from the body through exhalation. This process ensures that our body cells receive the oxygen they need for energy production and remove the waste product, carbon dioxide.
The exchange of gases primarily occurs in the alveoli, tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the air and the blood. This exchange is facilitated by the difference in partial pressures of these gases in the alveoli and the blood. Hemoglobin in the red blood cells plays an important role in transporting oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carrying carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation. Understanding these processes is essential for NEET students as they form the basis of respiratory physiology and are vital for the proper functioning of the human body.
| NEET 2025 Exam Important Links | |
|---|---|
| NEET 2025 Updated Syllabus | Best Books for NEET 2025 |
| Biology Preparation | Chemistry NEET Preparation |
| NEET Preparation tips for 2025 | NEET Result 2024 |
Breathing and Exchange of Gases NEET MCQ
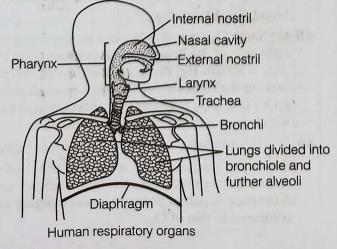
Lower invertebrates like sponges, coelenterates, flatworms, etc., exchange \( \mathrm{O}_{2} \) with \( \mathrm{CO}_{2} \) by simple diffusion over their entire body surface. Earthworms use their moist cuticle and insects have a network of tubes called trachea. Specialised vascular structures called gills are used by most aquatic arthropods and molluscs, whereas vascularised bags called lungs are used by terrestrial forms.
Enhance your preparation with Arexiq’s Mock Test Series where we provide solutions to various MCQs like we provide in this post “Breathing and Exchange of Gases NEET MCQ”. Our expert teachers explain the concepts thoroughly, making it easy for you to understand. We offer many types of questions ensuring a clear grasp of concepts.
FAQs about Breathing and Exchange of Gases for NEET
1.What is the primary function of breathing?
Answer. The primary function of breathing is to supply the body with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
2. Where does the exchange of gases occur in the lungs?
Answer. The exchange of gases occurs in the alveoli, tiny air sacs in the lungs.
3. What role does hemoglobin play in the exchange of gases?
Answer. Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and carries carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs.
4. Why is the exchange of gases important?
Answer. It is essential for providing oxygen for cellular respiration and removing carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism.
5. How does the difference in partial pressures facilitate gas exchange?
Answer. The difference in partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli and blood drives the movement of these gases, allowing efficient exchange.
6. Why is the exchange of gases important for the body?
Answer. The exchange of gases is crucial for providing oxygen to the body’s cells for energy production and removing carbon dioxide, a metabolic waste product.
7. How is carbon dioxide transported in the blood?
Answer. Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood mainly in the form of bicarbonate ions, but also bound to hemoglobin and dissolved in plasma.
8. What is the significance of the partial pressure of gases?
Answer. Partial pressure determines the direction and rate of gas exchange. Oxygen moves from areas of higher partial pressure (in the alveoli) to lower partial pressure (in the blood), and carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction.
9. How does the body regulate breathing?
Answer. Breathing is regulated by the respiratory center in the brainstem, which responds to changes in blood levels of carbon dioxide, oxygen and pH.
10. What is the role of the diaphragm in breathing?
Answer. The diaphragm is a major muscle involved in breathing. Its contraction and relaxation change the volume of the chest cavity, facilitating inhalation and exhalation.


