
Body Fluids and Circulation NEET Biology MCQ with Answers
Body fluids and circulation are important aspects of the human body that ensure the proper functioning of organs and tissues. The primary body fluid is blood, which consists of plasma and blood cells. Plasma is a straw-colored fluid that contains water, proteins, salts and nutrients. Blood cells include red blood cells (RBCs) that carry oxygen, white blood cells (WBCs) that fight infections and platelets that help in blood clotting. Blood circulates through the body via blood vessels, which include arteries, veins and capillaries. The heart acts as a pump, ensuring continuous blood flow through these vessels.
The circulatory system is divided into two main types: systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation. Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart to all body tissues and returns deoxygenated blood to the right side of the heart. Pulmonary circulation, on the other hand, transports deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs for oxygenation and then brings oxygenated blood back to the left side of the heart. This dual system ensures that oxygen and nutrients are delivered to cells while waste products are removed efficiently.
| NEET 2025 Exam Important Links | |
|---|---|
| NEET 2025 Updated Syllabus | NEET Eligibility Criteria 2025 |
| Biology Preparation | Chemistry NEET Preparation |
| NEET Preparation tips for 2025 | NEET Result 2024 |
Body Fluids and Circulation NEET MCQ
Body fluids and circulation are fundamental topics in the NEET syllabus, as they form the basis for understanding the human body’s physiological functions. Blood, the primary body fluid, transports essential substances like oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells and removes waste products like carbon dioxide and urea. This transport system is important for maintaining homeostasis and overall health. The circulatory system, which includes the heart, blood vessels and blood, ensures efficient distribution of these substances, making it vital for the functioning of various organs and tissues.
Understanding the principles of body fluids and circulation helps NEET aspirants grasp how the human body maintains internal balance and responds to physiological changes.
MCQs
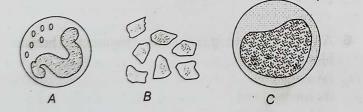
They are non-nucleated, round or oval-shaped cells which are produced from megakaryocytes. They are much smaller than RBC. Blood platelets are the source of thromboplastin, necessary for blood clotting and thus, they are known as thrombocytes.
Enhance your preparation with Arexiq’s Mock Test Series where we provide solutions to various MCQs like we provide in this post “Body Fluids and Circulation NEET MCQ”. Our expert teachers explain the concepts thoroughly, making it easy for you to understand. We offer many types of questions ensuring a clear grasp of concepts.
FAQs about Body Fluids and Circulation
What are the main components of blood?
Answer. Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs) and platelets.
2. What is the function of red blood cells?
Answer. Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and bring carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation.
3. How does the heart pump blood?
Answer. The heart pumps blood through rhythmic contractions, pushing blood through the circulatory system of arteries and veins.
4. What is systemic circulation?
Answer. Systemic circulation is the pathway in which oxygenated blood is transported from the heart to the rest of the body and deoxygenated blood is returned to the heart.
5. What is pulmonary circulation?
Answer. Pulmonary circulation is the movement of deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation and back to the heart with oxygenated blood.
6. Why are platelets important?
Answer. Platelets are important for blood clotting, which prevents excessive bleeding when injuries occur.


