
Chemical Coordination and Integration NEET Questions
Chemical Coordination and Integration involve the regulation of various functions in the human body through hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands. These glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream, which then travel to target organs or tissues to control activities such as growth, metabolism and reproduction. Unlike the nervous system, which provides fast and short-term responses, hormonal coordination offers slower but longer-lasting effects, ensuring the body’s internal environment remains stable.
The endocrine system works closely with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis or balance, in the body. While the nervous system provides quick responses to changes, hormones offer slower but long-lasting effects. Understanding the roles of different hormones and how they interact is vital for mastering this topic.
| NEET 2025 Exam Important Links | |
|---|---|
| NEET 2025 Updated Syllabus | How to read NCERT Biology for NEET |
| Biology Preparation | NEET Eligibility Criteria 2025 |
| NEET Preparation tips for 2025 | NEET Result 2024 |
Chemical Coordination and Integration NEET Questions
In the NEET syllabus, understanding chemical coordination is important because it helps in grasping how the body maintains homeostasis and responds to changes. Key endocrine glands like the pituitary, thyroid and adrenal glands are covered, along with their specific hormones and functions.
Chemical Coordination and Integration NEET Questions
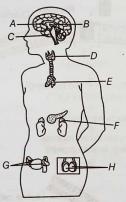
Enhance your preparation with Arexiq’s Mock Test Series where we provide solutions to various MCQs like we provide in this post “Chemical Coordination and Integration NEET MCQ”. Our expert teachers explain the concepts thoroughly, making it easy for you to understand. We offer many types of questions ensuring a clear grasp of concepts.
FAQs about Chemical Coordination and Integration
Q1: What is chemical coordination in the human body?
Answer: Chemical coordination refers to the regulation and control of body functions through hormones secreted by the endocrine glands.
Q2: What are hormones?
Answer: Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by endocrine glands and travel through the bloodstream to target organs, where they regulate various physiological processes.
Q3: Which gland is known as the “master gland” and why?
Answer: The pituitary gland is known as the “master gland” because it controls the function of other endocrine glands in the body.
Q4: What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
Answer: Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, while exocrine glands release their secretions through ducts to specific locations (e.g., sweat glands, salivary glands).
Q5: What role does the thyroid gland play in chemical coordination?
Answer: The thyroid gland produces hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which regulate metabolism, growth and development.
Q6: Why is understanding chemical coordination important for NEET?
Answer: Understanding chemical coordination is important for NEET as it covers important concepts related to the functioning of the human body, which are frequently tested in the exam.


