
Mineral Nutrition NEET Questions with Answers
Mineral Nutrition in Plants: Mineral nutrition is important for the growth and development of plants, as it involves the absorption and utilization of minerals from the soil. These minerals, categorized into macronutrients (e.g., nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) and micronutrients (e.g., iron, manganese, zinc), are vital for various physiological processes. Macronutrients are required in larger quantities and play key roles in processes like photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and cell division, while micronutrients, needed in smaller amounts, are essential for enzyme function and other metabolic activities.
Importance in Human Nutrition: For NEET aspirants, understanding mineral nutrition is equally important for human physiology. Essential minerals like calcium, potassium and iron contribute to bone health, nerve function and oxygen transport, respectively. Deficiencies or imbalances in mineral intake can lead to various health issues, such as anemia (iron deficiency), osteoporosis (calcium deficiency), or muscle cramps (potassium deficiency). Hence, a balanced diet rich in both macro and micronutrients is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing diseases.
| NEET 2025 Exam Important Links | |
|---|---|
| NEET 2025 Updated Syllabus | How to read NCERT Biology for NEET |
| Biology Preparation | NEET Eligibility Criteria 2025 |
| NEET Preparation tips for 2025 | NEET Result 2024 |
Mineral Nutrition NEET Questions with Answers
“Mineral Nutrition” is an important topic in the NEET syllabus as it covers the essential minerals required for plant growth and development, highlighting their roles in physiological processes. Understanding mineral nutrition is vital for grasping how plants absorb, transport, and utilize minerals from the soil, which directly impacts agricultural practices and food production.
Mineral Nutrition NEET Questions with Answers
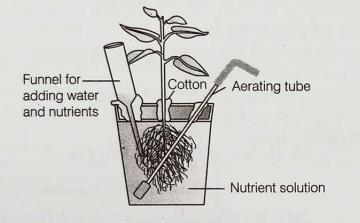
Choose the correct option.
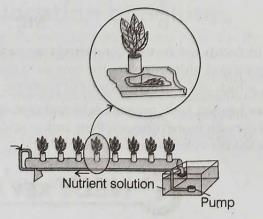
The solution flows down the tube and returns to the reservoir due to gravity not suction pressure. A pump circulates the nutrient solution from a reservoir to the elevated end of the tube.
Rest all options are correct.
Enhance your preparation with Arexiq’s Mock Test Series where we provide solutions to various MCQs like we provide in this post “Mineral Nutrition NEET MCQ”. Our expert teachers explain the concepts thoroughly, making it easy for you to understand. We offer many types of questions ensuring a clear grasp of concepts.
FAQs
- What is mineral nutrition in plants?
Answer. Mineral nutrition refers to the absorption, distribution and utilization of inorganic substances or minerals by plants. These minerals are essential for various physiological and biochemical processes.
- Why are minerals essential for plants?
Answer. Minerals are crucial for plants because they play vital roles in several physiological processes such as photosynthesis, respiration and enzyme activation. They also contribute to the structural components of cells.
- What are macronutrients and micronutrients?
- Macronutrients are minerals required by plants in larger quantities. Examples include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg) and sulfur (S).
- Micronutrients are required in smaller amounts. Examples include iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), boron (B) and chlorine (Cl).
- What is the difference between mobile and immobile nutrients?
- Mobile nutrients can move from older tissues to newer ones when there is a deficiency. Examples include nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
- Immobile nutrients remain in the older tissues, leading to deficiency symptoms in newer tissues. Examples include calcium, sulfur and iron.
- What are the symptoms of mineral deficiency in plants?
- Nitrogen Deficiency: Yellowing of older leaves (chlorosis), stunted growth.
- Phosphorus Deficiency: Dark green or purplish discoloration of leaves, delayed flowering.
- Potassium Deficiency: Browning of leaf edges (marginal necrosis), weak stems.
- Calcium Deficiency: Deformed leaves, blossom-end rot in fruits.
- Iron Deficiency: Interveinal chlorosis (yellowing between leaf veins) in young leaves.
- How do plants absorb minerals from the soil?
Answer. Plants absorb minerals from the soil through their root hairs. The minerals are taken up in ionic forms, such as nitrate (NO₃⁻), ammonium (NH₄⁺), phosphate (H₂PO₄⁻) and potassium (K⁺). The absorption process involves both passive and active transport mechanisms.


